
[+] Vulnerability Overview
Identifier: CVE-2025-5777 (“CitrixBleed 2”)
Disclosure Date: June 17, 2025 via Citrix security bulletin CTX693420; scope updated June 23, 2025
Nickname: “CitrixBleed 2” (inspired by CVE-2023-4966)
Severity: CVSS v4.0 9.3 (Critical)
[+] Executive Summary
In June 2025, security researchers identified a critical vulnerability affecting Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances. The flaw enables remote attackers to leak sensitive memory contents without authentication by exploiting improper input validation in the authentication endpoint. The vulnerability threatens exposure of session tokens, user credentials, and system secrets.
[+] Impact
- Pre-authentication remote memory disclosure in Citrix NetScaler ADC and Gateway appliances
- Leaked memory fragments may include session tokens (including nsroot), credentials in plaintext, authentication cookies, and sensitive data
- Attackers can hijack authenticated sessions and bypass MFA
- Over 11.5 million attack attempts observed; CISA added CVE-2025-5777 to Known Exploited Vulnerabilities Catalog on July 10/14, 2025
[+] Attack Vector & Complexity
- Attack Vector: Remote, unauthenticated access via HTTP POST to
/p/u/doAuthentication.do - Complexity: Low - no credentials needed; trivial to script repeated requests
- Authentication: Not required; malformed login parameter triggers vulnerability
[+] Affected Versions
Citrix NetScaler ADC / NetScaler Gateway:
| Version | Fixed Version |
|---|---|
| 14.1 | 14.1-43.56 or later |
| 13.1 | 13.1-58.32 or later |
| 13.1-FIPS / NDcPP | 13.1-37.235 or later |
| 12.1-FIPS | 12.1-55.328 or later |
EOL versions (12.1 and 13.0) are not patched and remain vulnerable; upgrade strongly recommended.
[+] Technical Details
The /p/u/doAuthentication.do endpoint processes authentication POST requests. When attackers provide the login parameter without an equals sign or value (e.g., “login” alone), backend C code fails to initialize the memory variable. The resulting XML response injects leftover stack memory in the <InitialValue> element.
Attack Sequence:
- Unauthenticated malformed request
- Memory leak via
<InitialValue>in response - Attacker repeats to gather data fragments (~127 bytes per request)
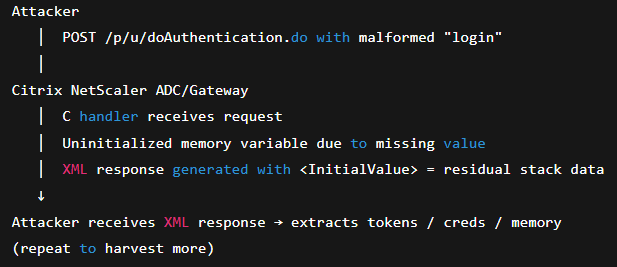
Example Malicious Request:
POST to /p/u/doAuthentication.do with parameter “login” (no equals sign or value)
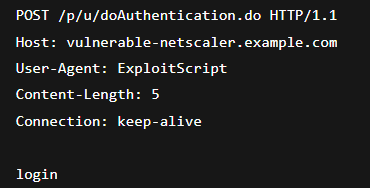
Example Response:
XML containing leaking stack memory in <InitialValue> tag, repeatable to harvest multiple fragments.
[+] Mitigation & Response
1. Patch Immediately
Upgrade to fixed versions:
- 14.1 -> 14.1-43.56 or later
- 13.1 -> 13.1-58.32 or later
- FIPS/NDcPP, 12.1-FIPS -> apply corresponding fixed builds
No effective mitigation exists other than patching; WAF signatures may help but are not reliable.
2. Terminate Active Sessions Post-Upgrade
kill icaconnection -all
kill pcoipConnection -all
This ensures previously leaked tokens are invalidated.
3. Monitor & Hunt
- Review logs for exploitation attempts
- Deploy IDS rules to detect malformed
/p/u/doAuthentication.dorequests - Use anomaly analytics to catch suspicious behavior
4. Network Controls
- Restrict external access to NetScaler appliances (VPN endpoints or AAA servers)
- Segment appliance access behind VPN or firewall
- Limit exposure surface
5. Follow-Up Actions
- Engage forensic review if suspicious activity detected
- Rotate credentials/tokens if session hijacking suspected
- Use NetScaler Console insights or ADM file-integrity monitoring for changes
[+] Honeypot Analysis
Deployment & Setup
On June 25th, we deployed a fully interactive Citrix NetScaler honeypot designed to mimic a vulnerable Gateway environment.
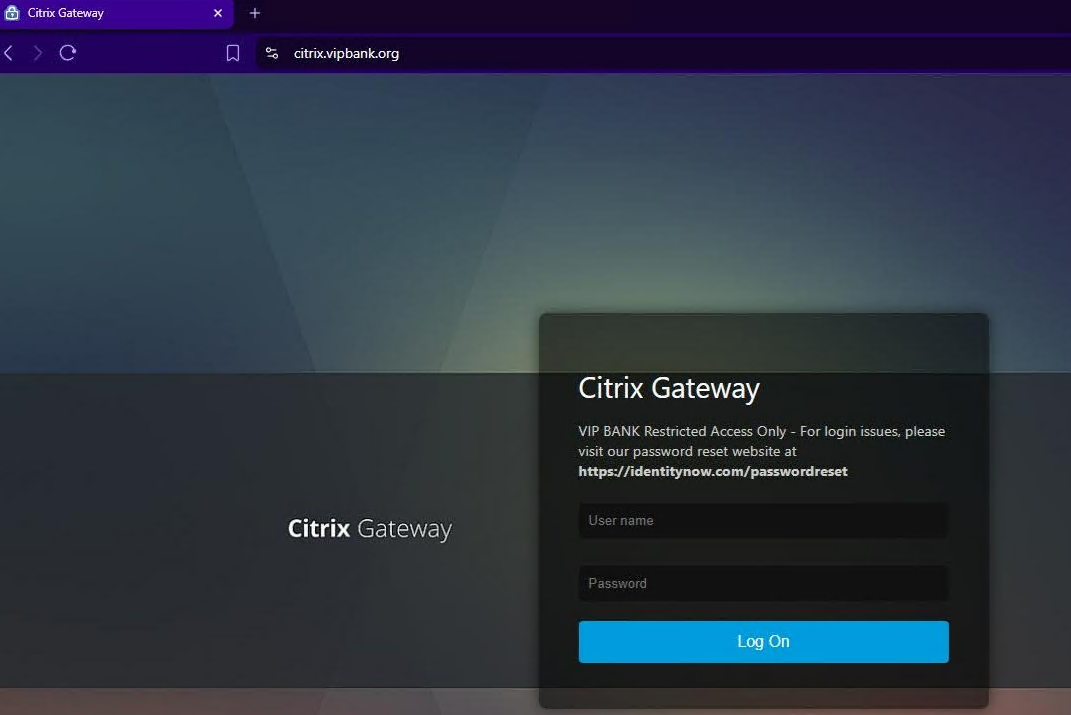
The honeypot:
- Listens on port 443
- Reproduces authentic login portal including
/vpn/index.html - Includes realistic HTML/CSS/JavaScript user interface
- Mimics key Citrix-specific behaviors
- Uses domain
vipbank.orgwith LetsEncrypt SSL certificates
Backend Simulation
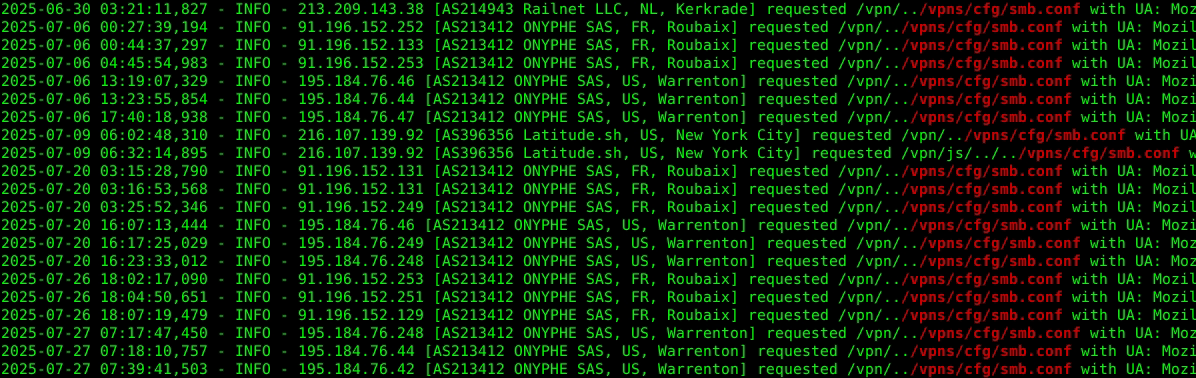
Beyond the front end, the honeypot exposes simulated backend vulnerabilities:
- Requests to
/menu/ss,/vpn/../vpns/cfg/smb.conf,/rpc/../../../../../../../../etc/passwdreceive plausible outputs - Interactions with
/p/u/doAuthentication.doreceive craftedapplication/vnd.citrix.authenticateresponse-1+xmlpayloads - XML responses follow real NetScaler schema including
<PostBack>/p/u/doAuthentication.do</PostBack>and<CancelPostBack>/p/u/doLogoff.do</CancelPostBack>elements - Scanners and exploit scripts believe they interact with live, vulnerable appliance
Intelligence Gathering
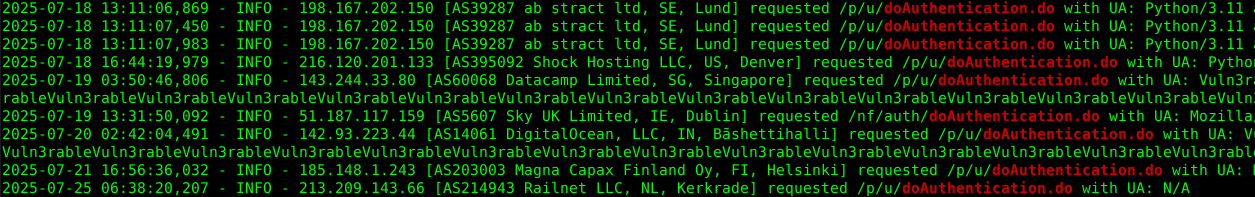
Every incoming connection is fingerprinted via ipinfo.io enrichment with:
- Organization details
- Geographic location
- Reverse DNS information
Display: Live on-screen for hits to / and /vpn/index.html; fully logged in netscaler_honeypot.log
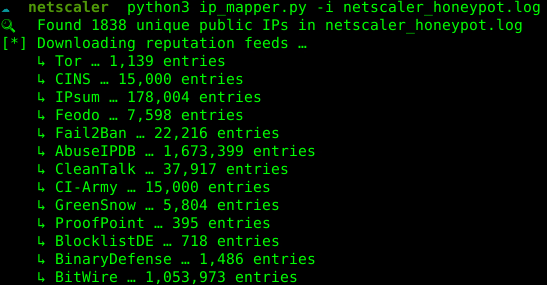
Persistent Storage: Companion toolset ip_mapper.py:
- Parses honeypot log
- Normalizes unique IP addresses
- Enriches with metadata
- Saves to
ips.db(SQLite database) - Enables long-term analysis and threat intelligence correlation
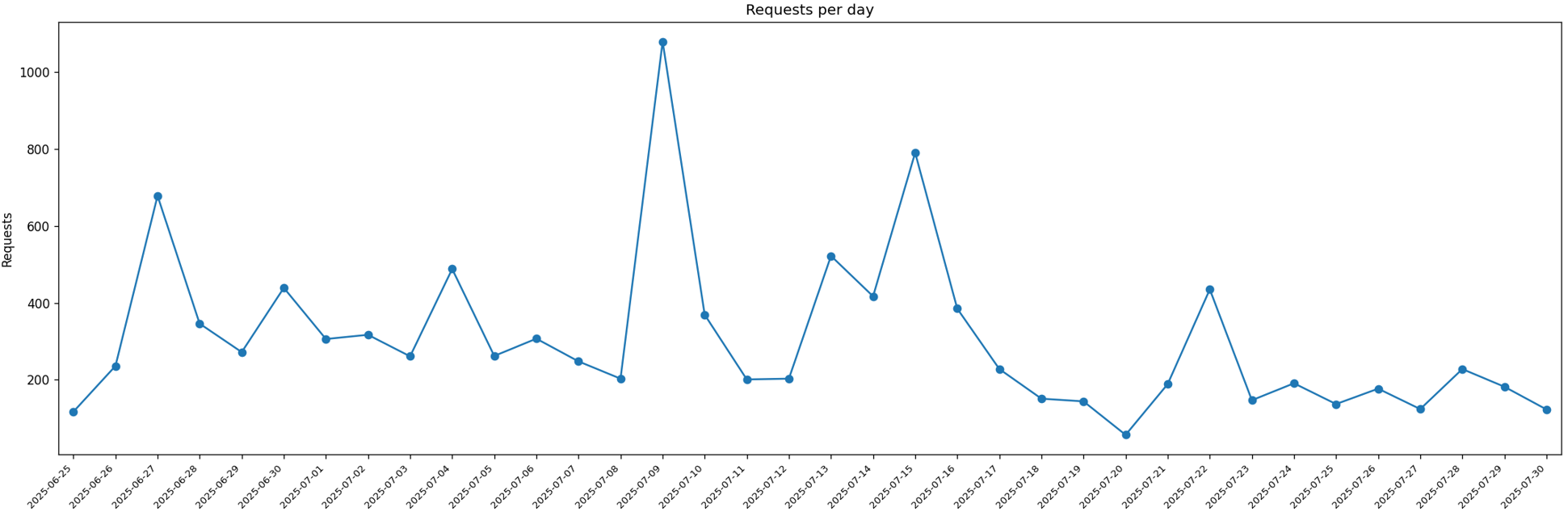
Request Statistics
Threat Actor Activity
The honeypot also attracted threat actors looking to exploit CVE-2019-19781 (an earlier Citrix vulnerability).
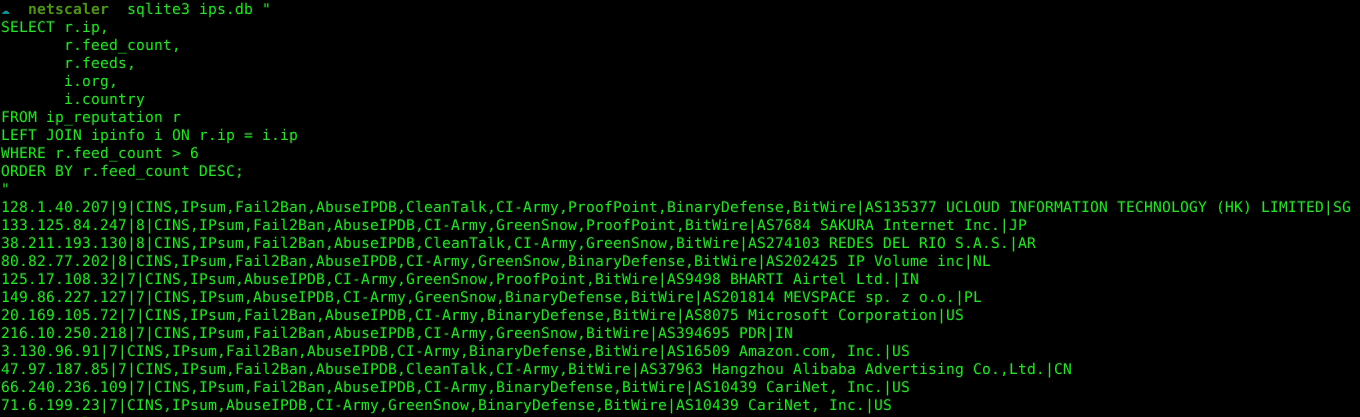
[+] ips.db SQLite Database
Purpose
Acts as structured repository of every unique IP address touching the honeypot, enabling long-term threat analysis.
Data Structure
Two main tables:
-
ipinfo: Canonical record of each IP with enrichment data
- ASN/organization
- Country and city
- Reverse DNS hostname
- First seen timestamps
-
ip_reputation: Logs threat intelligence lookups
- Tracks reputation across OSINT feeds
- Correlates single attacker IPs over time
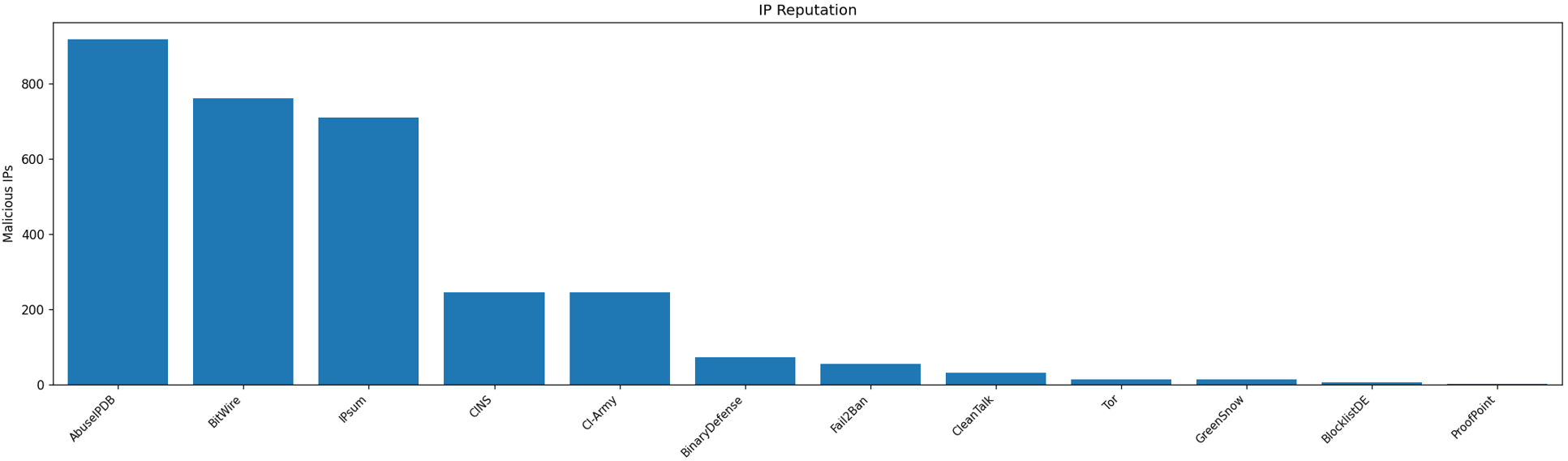
Analysis Capabilities
- Track IPs probing honeypot weeks apart
- Identify whether IP belongs to cloud provider, botnet, or opportunistic researcher
- Build pivot tables of active regions and hosting providers
- Generate heatmaps of attacker origins and behavior patterns
- Highlight which organizations/ASNs responsible for majority of attacks
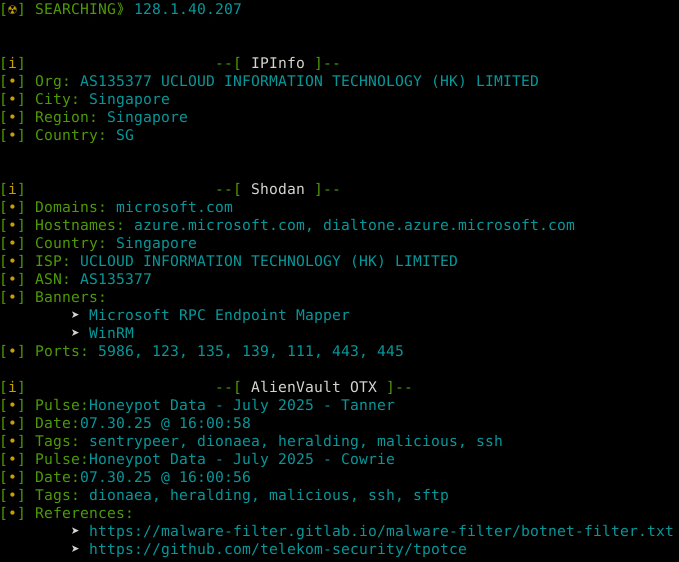
[+] Top Offender Analysis
IP: 128.1.40.207
This address was identified as responsible for significant attack traffic against the honeypot, labeled in 6+ reputation feeds.
[+] Downloadable Resources
- Raw Logs: netscaler_honeypot.log
- IP Database: ips.db (GitHub repository)
Both files available for research and threat intelligence purposes.
[+] Key Takeaways
CVE-2025-5777 represents a critical pre-authentication vulnerability with trivial exploitation requirements. Organizations must prioritize immediate patching, session termination, and enhanced monitoring to defend against this widespread threat.